🔑 Using Secure Keys for GitHub SSH Operations #
In this post on using FIDO U2F for GitHub SSH we see how you can set up secure keys for pushing code update to your GitHub repositories. Git offers version tracking and assists collaboration on coding projects. GitHub is currently the best known service offering git repo hosting. The recent rise of the JAMStack and other trends have made committing code to a git service an essential stage in the continuous integration process.
Authentication technology has also moved on as signing in with SSH passwords got replaced with using PGP keys. Taking it a step further, you can now use FIDO U2F secure keys to authenticate SSH transactions. The added security advantage is that the USB key has to be with you physically when you commit. In this post, we look at how you can set up secure keys for GitHub and also some SSH configuration settings. I hope this is something you will find useful.
😕 What is FIDO U2F? #
FIDO U2F keys are hardware tokens used in Multifactor authentication . Like 2FA authenticator app codes, they offer second factor authentication (2FA) though FIDO U2F keys are less susceptible to phishing attacks than those authenticator app codes. As an example, of when you might use FIDO U2F keys, you can harden your Twitter, Gmail and Facebook or even GitHub account by enabling FIDO U2F and using that as your preferred login method. Typically, you plug in the USB key as you log in and have to tap it to complete the login. We'll see here how using FIDO U2F for GitHub SSH can secure your push and fetch operations.
⚙️ How to Create an SSH Secure Key for GitHub #
Using FIDO U2F for GitHub SSH #
- You can use an existing FIDO U2F key, but if you don't yet own one you will need to buy one. YubiKey make a number of keys, some of them much more expensive than others. The basic and relatively inexpensive Security Key models are fine to use here. You can also use other brands.
-
Check you have a compatible version of OpenSSH installed by running the
command:
-
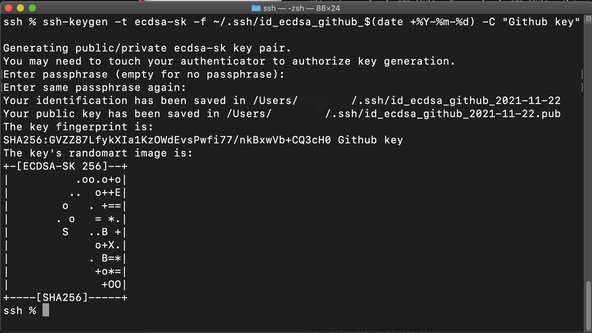
Place your FIDO U2F key in a free USB port and type the following
command to start the one-time setup:
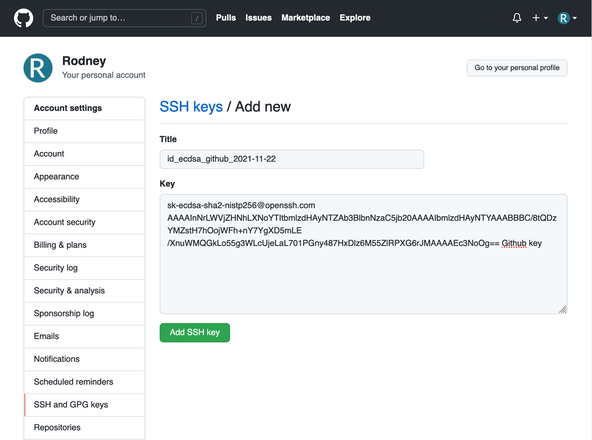
ed25519-skin place ofecdsa-skabove because of association of ECDSA keys with government agencies. Your own choice will depend on your threat model as well as what your own key supports. - Log in to GitHub, click your avatar in the top right and select Settings. Then from the menu on the left select SSH and GPG keys then click the New SSH key button.
-
In the new screen that appears, enter something to help you identify
your key in the Title, you might want to use the filename for your
public key. Next, get the public key by typing the following command in
the Terminal:
-
Finally, let's test the new key. Place the FIDO U2F key into a free USB
port and run the test command:
Finishing Off #
For some best practices on SSH client keys, see the Mozilla guide .
🔨 SSH Config #
Since we are hardening the login method, we can also harden the SSH configuration. I based this configuration off Dr Duh's configuration .
1 # https://github.com/drduh/config/blob/master/ssh_config2 # https://linux.die.net/man/5/ssh_config3 Host github.com4 User git5 ControlMaster no6 IdentitiesOnly yes7 IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_ecdsa_github_YYYY-mm-dd8 MACs [email protected],[email protected],[email protected],hmac-sha2-512,hmac-sha2-256,[email protected]9 Host *10 AddressFamily inet11 HashKnownHosts yes12 VisualHostKey yes13 PasswordAuthentication no14 ChallengeResponseAuthentication no15 StrictHostKeyChecking ask16 VerifyHostKeyDNS yes17 ForwardAgent no18 ForwardX11 no19 ForwardX11Trusted no20 ServerAliveInterval 30021 ServerAliveCountMax 224 KexAlgorithms [email protected],diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha256
This prefers IPv4 connections over IPv6, disables password login as well as
some other hardening measures such as limiting the allowed encryption ciphers
and message authentication algorithms. Be sure to update the path to your
GitHub key in line 7 to match the path of the key you just created. The
settings in lines 3 – 8 apply just to GitHub
SSH connections. The remaining ones apply to any other SSH connection, so these
may need tweaking to work with any other services you use. Be sure to test all connections
with this new configuration.
🗳 Poll #
🙌🏽 Using FIDO U2F for GitHub SSH: What we Learned #
In this post we looked at:
- why you would want to use a FIDO U2F key for GitHub SSH operations,
- how to create an SSH secure key for GitHub,
- a hardened SSH configuration.
I do hope there is at least one thing in this article which you can use in your work. You may also want to see GitHub's own documentation on setting up secure SSH keys .
🏁 Using FIDO U2F for GitHub SSH: Summary #
What is GitHub secure key SSH? #
- Traditionally, for connecting to a remote system using SSH, just a password was used. Best practice has since evolved and now, typically, we use a cryptographic key in place of a password. This takes the form of public key cryptography, where a public key is shared to the remote service and the user authenticates using their private key. Secure keys add additional protection. There is only a single FIDO U2F hardware token authorized to authenticate requests, which cannot easily be cloned. Since the token has to be with the user at the time of authentication, unauthorized access to systems is made much harder.
Does GitHub accept FIDO U2F SSH keys for operations? #
- Yes. GitHub has allowed FIDO U2F secure key SSH operations, using YubiKey Secure Keys as well as other brands, since May 2021. You need OpenSSH 8.2 or higher on your machine to create a suitable SSH key, as well as a compatible FIDO U2F key. The cheaper YubiKey FIDO U2F hardware tokens as well as other brands will work.
How do you create a FIDO U2F SSH key for GitHub? #
- You can create a FIDO U2F SSH key for GitHub using the common OpenSSH command line utility. Just use the -t esdsa-sk flag to create an ECDSA secure key. During the process, you will be asked to touch the key and also enter a password. Once set up, whenever you push to your GitHub repo, you will need the same FIDO U2F token.
🙏🏽 Using FIDO U2F for GitHub SSH: Feedback #
Have you found the post useful? Would you prefer to see posts on another topic instead? Get in touch with ideas for new posts. Also, if you like my writing style, get in touch if I can write some posts for your company site on a consultancy basis. Read on to find ways to get in touch, further below. If you want to support posts similar to this one and can spare a few dollars, euros or pounds, please consider supporting me through Buy me a Coffee.
🔑 I put together some details on how you can create a secure key for SSH GitHub transactions using your FIDO U2F USB key 🧵
— Rodney (@askRodney) November 24, 2021
- FIDO U2F keys offer secure second factor authentication
- the FIDO U2F key stores part of the SSH key
- you need the hardware token to push to GitHub
pic.twitter.com/zMSeqE04z5
Finally, feel free to share the post on your social media accounts for all your followers who will find it useful. As well as leaving a comment below, you can get in touch via @askRodney on Twitter and also askRodney on Telegram . Also, see further ways to get in touch with Rodney Lab. I post regularly on SvelteKit as well as security-related topics. Also, subscribe to the newsletter to keep up-to-date with our latest projects.


